Tech terms can be confusing and there are always new terms emerging. This guide will help you easily find definitions for common tech terms that you see day to day and terms you might hear us use when we describe Webformix services, or when you are getting support.
Table of Contents
Click on the link below to navigate to a section alphabetically, or you can use the keyboard shortcut “ctrl+f” to open a search bar and type the specific term you are looking for. You can also navigate simply by scrolling!
1-9: Tech Terms Defined
3G: Third generation cellular network with an average speed of 6 Mbps; 3G networks shut down in 2021
404 Error: You see this error when a webpage is not found as a result of a “dead link” (a link that leads to a page that is no longer there); Results from a webpage that has been deleted
4G: Fourth generation cellular network; Speeds up to 60 Mbps with 12-20 Mbps on average
5G: Fifth generation cellular network; Speeds up to 1000 Mbps with 40-60 Mbps on average; 5G conspiracies have erroneously claimed that it could be hazardous to health (see video below for more on that)
A: Tech Terms Defined
Account Hijacking: Occurs when a hacker gains access to a person’s account(s) and then changes login credentials so the user can no longer access their account; Typically starts through phishing or spoofing scams that give a hacker access to a person’s email account [1]
Activation Key: Code used to register or activate software or services
Activity Tracker: Device that monitors health-related activities such as exercise, steps, sleep, and/or heart rate and stores the data in an app that shows the user results and health insights. Examples: FitBit, Oura Ring, Google Fit
Ad Blocker: Computer software or internet browser plug-in that blocks advertisements like pop-ups
Adobe Acrobat: Software that allows you to read and edit PDF (document) files
Adobe Flash: Multimedia software used for animation, games, and app development; Animation, games, and apps are embedded on a website; Discontinued, but emulators can be used to view; Popularized and innovated by Homestarrunner.com (an internet-based cartoon and game with a cult following)
Adobe Photoshop: Software for editing and creating graphics
Advanced Threat Detection (ATD): Cybersecurity tools that go beyond the basics and conducts deep threat analyses such as checking downloads, network traffic, and user activities [1]
Adware: Free software or apps that contain paid advertisements; Often collects your internet browsing information in order to target ads towards you; Can be legitimate like in free trials or can be spyware that compromises your privacy and security, may also come in the form of preinstalled bloatware [1]
Algorithm: Defined sequence of instructions for solving a mathematical problem in computing; Example: Creates Netflix recommendations, search engine website rankings to determine what sites are most relevant to your search words
Amazon: Giant corporation that includes an e-commerce platform, technological services, video streaming, cloud storage, and more
Amazon Web Services (AWS): Cloud-based remote computing service bundle launched in 2006; Helps to consolidate server power and storage [1]
Android: Open-source mobile device operating system
Apple: One of the world’s largest technology companies that famously makes devices that are incompatible with Microsoft and Android products; Maker of the iPhone, iPad, Macbook, and more; Have faced much scrutiny for the planned obsolescence of their devices
Application (App): A type of software program designed to run on a mobile device; Apps have started to replace websites such as people using the Facebook app versus using the Facebook website. They can also be games and utilities. Many computers now feature app stores instead of the old model of people buying software on discs and then installing them.
Application Programming Interface (API): Software intermediary that allows two applications to talk to each other
Artificial Intelligence (AI): A computer system that is to some extent capable of learning and adapting its behavior based on external inputs; Mimics cognitive functions such as learning and problem solving; Examples: Search engines, Netflix video recommendations; Siri or Alexa voice assistants; self-driving cars [2]
Augmented Reality (AR): Augmented reality is not immersive like virtual reality; Instead of replacing reality, AR adds to reality with a digital overlay. It creates a much more engaging and interactive experience, but you remain aware and connected to the real world. Examples: Smart glasses like Google Glass and Microsoft HoloLens, games and apps like Pokemon Go.
Authentication: The process of verifying a user’s authentic identity
Autocomplete: Automatically completes words as you type them, and example is Google’s Smart Compose in Gmail; Not always correct, similar to predictive text that suggests common words as you start typing
Autofill: Automatically fills fields in website forms with information that your browser has saved such as your name, address, email, and phone number; Not always correct
Autocorrect: Automatically corrects spelling errors, sometimes incorrectly
B: Tech Terms Defined
Backhaul: Wireless communications system that transports data in a sub-network that originates from the main communications tower; Helps to distribute stable fixed wireless internet signals further away from the main tower
Bandwidth: Data carrying capacity or data transfer speed of a network connection; Bit-rate measurement of a network’s capacity.
Beta (Version): If you are using a “beta” version, it usually means that it is a trial version that is still in development (similar to a pre-release where bugs are still being worked out)
Binary: Base-2 numbering system that uses the numerals 0 and 1 for counting; Used by computers to perform calculations [1]
Biometrics: Technology that uses biological factors like your eye, face, or fingerprint in order to verify your identity; Commonly used to unlock phones
Bit (b): The “speed” (bandwidth) of an internet connection is typically measured in bits per second. When referring to bandwidth, bits per second are constrained by the width of the “pipe,” not the “speed” of the packets. An example is if the packets are moving at the speed of light down fiber lines, and the speed of light is a constant. See also “Bits and Bytes: Measuring Bandwidth vs File Size”
Bitcoin: Cryptocurrency; Decentralized digital currency used in peer-to-peer transactions; Unregulated; Obtained through “mining” and tracked on a digital ledger called a “blockchain“
BitTorrent: A peer-to-peer protocol for file sharing; Famous for use in pirating media
Blacklist: Opposite of whitelist; To mark a particular website or email address as malicious or spam and block it
Blind Carbon Copy (BCC; Email): When you enter an email address in the “BCC” line of an email, the person(s) in the “To” address line will not see that a copy of the email was sent to the “BCC” recipient(s)
Bloatware: Applications and files that are not necessary for computer functionality but come pre-installed on computers to promote their use
Blockchain: Digital database that acts as a ledger to track and record the creation and transaction of cryptocurrencies
Blog: A blog is a website or part of a website where articles are published
Blu-Ray Disk: High-capacity disk for videos that came just after DVDs and supports higher video formats than a DVD with higher resolutions; Requires a special Blu-Ray disk player [1]
Bluetooth: Wireless technology that operates on the 2.4 GHz band; Allows you to wirelessly connect devices; Examples: Wireless headphones or earpieces, connecting your phone to your computer or TV, file sharing between cell phones
Bookmark: To save a website in your browser so you can easily access it through a shortcut link
Bot: An automated program that replicated a human task; Can be used for good or bad. Examples: Chatbots for customer service, non-player characters in online games, spambots that send malicious emails [1]
Bounce (Email): If an email “bounces” that means that it is not delivered either due to an error like mistyping the email recipient’s address or because you have been blocked or marked as spam by the recipient
Browser (Web Browser; Internet Browser): A software application for accessing the world wide web; Examples: Microsoft Edge (replaced Internet Explorer), Google Chrome, Apple Safari, Brave, Firefox. More information “What is the Best Internet Browser in 2021?“
Browser Hijacker: Spyware or malware disguised as a browser plug-in that redirects users to unwanted websites and/or captures their sensitive personal data [1]
Browser History: A setting in your internet browser that records a log of all of the websites you visit
Buffering: Buffering is a process that seeks to avoid lag when media such as video is playing, to do this data is pre-loaded into your device’s memory so it can be accessed faster during playback. If too much data is pre-loaded, buffering can be problematic.
Bug Fix (Debug): A change to a program’s code to fix a glitch (bug)
Byte (B): There are 8 bits in a byte. The file size is typically defined in terms of bytes instead of bits. This makes an 8 Mbps (megabits per second) internet connection capable of downloading 1 MB in one second.
C: Tech Terms Defined
C Drive (C:): Main hard disk partition which contains the operating system and the related system files [1]
Cable Internet: A form of broadband internet access and it uses the same infrastructure as cable television; Usually integrated into the cable television infrastructure.
Cache: High-speed data storage and retrieval technique
Campaign Management System (CMS): Software for managing sales and marketing campaigns and tracking performance metrics
CAPTCHA: CAPTCHA stands for Completely Automated Public Turing Test To Tell Computers And Humans Apart. It is a puzzle such as an image or phrase that a user interacts with to demonstrate that they are an actual person and not a bot that could be trying to gain access to a system for malicious purposes
Carbon Copy (CC; Email): When you enter an email address into the “CC” line of an email, a copy of the email will be sent to that person as well as the main recipient, the main recipient will be able to see recipients in the “CC” line
Card Verification Value (CVV): Security code on the back of a credit or debit card; Used for verification when placing orders online
CAT Cable (3; 4; 5; 6; 7): There are five main types of ethernet cable. Cat3 cable is an ethernet cable used for voice and data communications in computer and telecommunication networks and transmits data at a speed of 10 Mbps. Cat4 cable provides 20 MHz of bandwidth with a data transfer rate of up to 16 Mbps. Cat5 and Cat6 cables are newer types of ethernet cables that help to deal with the issue of cross-talk or signal bleeding. Cat7 cable supports up to 10 Gbps and a bandwidth speed of 600 MHz [1].
Cellular Data: Also celled mobile data; Data that is transmitted over a cellular network to provide internet connectivity to smartphones
Cellular Phone: A phone that works using mobile wireless technology instead of copper telephone lines (landline)
Cellular Network: A network distributed over radio waves via transmitters on communication towers; Used for mobile data and telecommunications [1]
Certificate Authority (CA): A trusted third-party entity that issues digital security certificates and public keys to ensure public network connections are authentic and secure [1]
Chatbot: An automated response system with artificial intelligence that interacts with you as you enter prompts; Can be used for customer service
Cisco: A company that produces networking hardware and software for telecommunications, data, and computing
Clickbait: An article that uses an alarming title to get you to click on it but does not contain accurate or informative content; The publisher gains money from having you click it and the clickbait article may take you to a site that exposes you to security threats
Cloud: A metaphorical place on the internet that provides remote access for computing and storage; Examples: Google drive, GSuite, iCloud
Code: Instructions that are written in a language that computers can understand to create things like apps, websites, and software
Command (.CMD): A specific word or phrase that tells a computer what to do when it is entered in a command-line interface or shell [1]
Communications Satellite: A satellite in Earth’s orbit that receives and transmits communications data for use in satellite internet service, television, radio, and weather
Compact Disc (CD): Plastic disc that stores data (such as music) and is read using light
Content: General term used to refer to writing, images, and video that is published and shared online
Content Filtering: A program that prevents certain types of (generally harmful) content from being accessed
Control-Alt-Delete: Pressing these three keys on a keyboard simultaneously will give you the option to restart your computer or launch the task manager; Used when a computer freezes up to shut it down
Copy & Paste: Command used to duplicate content and place it in a new location: Keyboard shortcuts control+c for copy and control+v for paste
CPU (Central Processing Unit): The main processing unit of a computer that interprets instructions from software, located on the computer’s motherboard [1]
Crash: An event where an operating system stops functioning due to a problem such as hardware failure, corruption of critical data, or the system is not able to recover from an error without loss of data [1]
Credentials: Part of a certificate or authentication process that helps verify the authenticity of a user [1]
Crowdfunding: An online fundraising campaign used to fund business ventures or other endeavors
Cryptocurrency: Decentralized digital currency that is tracked in a blockchain; Unregulated. Examples: Bitcoin, Etherium, Dogecoin
Cursor: The arrow that appears on your computer screen and moves when you move your mouse (or follows finger movements on the trackpad of a laptop); Not present on tablets or smartphones with a touch screen
Cut & Paste: Command to remove content and place it in a new location; Keyboard shortcuts control+x for cut and control+v for paste
Cybersecurity: Measures that are taken to protect computers and networks from malicious activities, unauthorized activities, and unauthorized access; Involves detection of security threats, containment of security threats, and prevention. Examples: Firewalls, antivirus software, ad blockers
D: Tech Terms Defined
Dark Web: Websites with hidden IP addresses that cannot be found through search engines. Special software is needed to access them through an encrypted network [1]. The dark web is largely used for conducting illegal activities.
Data: Distinct pieces of digital information [1]
Data Center: A server repository for mass data storage and cloud storage [1]
Data Collection: The aggregation of information about user activity online; Provides businesses with useful information but can also create alarm and concern as to how the information is used for social engineering and the collection of sensitive data that can be breached by hackers [1]
Data Corruption: If data loses its integrity or becomes unreadable or unusable in some way, it is said to be corrupted. This can happen due to computer viruses altering files or due to software malfunctions [1].
Data Mining: The process of using algorithms to perform deep analysis on collected data to gain insights and perspectives that can help businesses make better decisions
DDoS Attack: A type of malicious attack where multiple hosts (imitation website users) overwhelm a website and force it to crash and lose functionality
Deepfake: Deepfakes are AI-modified videos that mask one person’s face over another person’s body. They can be used for harmless fun or for more dubious reasons. Deepfakes are not limited to video, they include audio as well. These altered videos and audio are concerning because they are largely being used to hurt others.
Deep Packet Inspection (DPI): Sophistic filtering mechanism that enables its users to track down, identify, categorize, reroute or stop packets with undesirable code or data [1]
Desktop: This is what you normally see when you turn on your computer, it will have icons for different files and programs
Desktop Computer: Another word for a PC, usually a computer that consists of a monitor and the “tower” part which contains the actual computer hardware
Developer: A person who uses code to create software, websites, apps, and more
Device Manager: A feature in the Windows control panel that is used to view and manage hardware devices that connect to your computer like headphones, USB keyboards, and optical mice.
Dial-Up Internet: Dial-up is very slow old-fashioned internet that works via phone lines. It is not in current use except in very rare circumstances and can only achieve speeds in the Kbps range which is thousands of times slower than modern internet services that have speeds in the Mbps to Gbps range.
Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA): Copyright regulations that apply to digital intellectual property
Disk Defragmenter: A utility program on a computer that consolidates fragmented files on the hard drive, by doing this, data retrieval is more efficient, and overall computer performance is improved [1]
Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) Internet: DSL internet provides internet service via telephone lines and manages traffic through DSLAMs. Further reading “Fixed Wireless Internet vs DSL Internet: Pros & Cons”
Digital Versatile Disc (DVD): A plastic disc that looks like a CD but contains a video instead of music; More commonly used than Blu-Ray but thought to be lower quality graphics
Direct Message (DM): Message sent directly between two users or a defined group of users; Same as a private message
Document (Doc): A file format generated by a word processor like Microsoft Word or Google Docs, generally contains text but may also include images and tables
Dogecoin: Cryptocurrency that started as a joke
Domain Name: The name and address of a website; Example: www.webformix.com
Dots Per Inch (DPI): A measurement of image resolution, specifically the number of dots that are displayed within a one-inch area; Higher DPI images have better resolution
Download: A download is a program, document, image, video, or another type of file that is copied from an online source onto your device’s storage
Doxing: Also spelled doxxing; The act of obtaining someone’s personal data and publicly divulging it online for malicious purposes such as harassing people, sending police to their house, or extortion
DSLAM (Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer): A networking device used to deliver DSL internet to customers and manage internet traffic; DSL internet speeds are generally lower the further you are from the DSLAM. Further reading “Fixed Wireless Internet vs DSL Internet: Pros & Cons“
E: Tech Terms Defined
E-Commerce: Online businesses that buy and sell products or services; See “How Does E-Commerce Work?“
Email: Electronic messaging system that operates over the internet; Email servers accept, forward, deliver, and store messages [2]
Embedded Object: An object that is published on one website but can be placed on another website such as the YouTube videos placed in this article
Encryption: An algorithm that changes text into a cipher text that requires an encryption key to decode. Many types of encryption exist, usually, the “key” is a password
Etherium: Decentralized digital currency (cryptocurrency) that is very popular like Bitcoin
Ethernet: Networking technologies for connecting devices on a local area network
Event Log: A log that stores data about network traffic, usage, and conditions, applicable for monitoring network security and monitoring users actions on a network [1]
Expansion Slot: A space on the motherboard of a computer where expansion cards with different features can be added, such as graphics cards, sound cards, or memory cards [1]
Extension: Can be synonymous with a plug-in; Software that adds or enhances the capabilities of a program but is not functional on its own [1]
External Hard Drive: A removable external storage device that provides additional storage space; Are less popular now that cloud storage is cheaply available
F: Tech Terms Defined
FaceTime: Apple’s video calling software that only works with iPhones; Non-iPhone users can make video calls via WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, Skype, or Google Duo
FCC (Federal Communications Committee): Federal body that governs communications; On their website, you can file communications related complaints and learn about online safety
Fiber Internet: Delivery of extremely high-speed internet service over fiber optic cable; Some networks may feature partial fiber in a hybrid system but a 100% fiber internet connection is not widely available outside of major cities
File: File is a very broad term, it is basically a container for things like software programs, documents, images, or video that contains all of the data a computer reads to create the visual interfaces we are familiar with
File Compression: To save storage space and allow for faster file transfer, the actual size of a file can be reduced and then returned to full size. Example: Zipped files
File-Sharing: Online platforms like BitTorrent allow people to share files with each other. Files can also be shared via email or cloud services.
Firefox: An internet browser made by Mozilla
Firewall: Software that can block data from certain locations or programs and prevent unauthorized network access
Firmware: Software that is embedded in a device to provide critical operating instructions
Fixed Wireless Internet: Internet service that utilized radio frequency for the propagation of the network (instead of phone lines for DSL or cable lines for cable internet). A radio antenna is mounted to the client’s roof and acquires internet signals from a nearby communication tower. The client location needs to have line of sight to the particular communication tower that the service provider has infrastructure on. Further reading “Top 5 Questions Fixed Wireless Internet Customers Ask When Signing Up“
Flaming: Hostile online interactions, often a bombarding of a particular user or post with abusive language
Freemium: A business model where a program or service offers a free version to entice users, and a paid version with expanded features
Freeware: Programs that are copyrighted but allow people to use them completely for free
G: Tech Terms Defined
Gaming: Gaming can refer to console gaming (Playstation, Nintendo, etc.) or online gaming done through a computer
Geolocation: Work through built-in GPS to locate devices; IP address, MAC address, and radiofrequency can also be used for geolocation
GHz (Gigahertz): Equivalent to one billion hertz
GIF: A short, low quality animated image
Gigabit (Gb): Measurement unit equivalent to one billion bits; “Gig speed” internet is measured in Gbps instead of Mbps because it is 1,000 times faster
Gigabyte (GB): Measurement unit equivalent to one billion bytes
GNU/Linux: A combination of operating system components and services, popular with developers and programmers but not normally used by the general public
Google: A tech giant that started off as a search engine and now offers email, an office suite comparable to Microsoft office but accessed online, cloud storage, online advertising and business resources, hardware like the Pixel phone, and more
Graphics Card (GPU): Graphics cards can be added to expansion slots on computers to improve the graphics display, they are also used for mining cryptocurrency and are popular for high-end gaming
H, I: Tech Terms Defined
Hacking: “Black hat” hacking is the malicious use of computer technology and social engineering to steal sensitive data, steal money, steal information, and perform other malicious activities. There is also “white hat” hacking which uses similar techniques as black hat hacking but is done lawfully for good purposes such as testing security systems.
Hard Disk Drive (HDD): Magnetic disk that rotates at high speeds; Used for computer storage space [1]
Hashtag (#): A type of tag used on social media to provide metadata (briefly explain the topic)
HDMI Cord: A cord for transmitting uncompressed data; Used to display a computer screen on a larger screen like a television or monitor or to connect a device like a Roku to a TV for streaming video
Hertz (Hz): A unit for measuring radio frequency or sound waves
Hibernate Mode: A power-saving mode for computers that retains information that was currently open but powers down functions, when turned back on, that information will be displayed again
High Definition (HD): A video resolution that is lower quality than Ultra-high definition but better quality than standard-definition; 720p or 1080p Video mode. See also “Wireless Internet Streaming Guide“
Homepage: The page that loads first when you open your internet browser. Each browser will have its own default homepage, but you can change it to whatever website you want in your browser settings.
Hosting (Website): A remote storage computer is used to store and maintain website data that is accessible via the internet [1]
HTML: A language used to display and create web pages [1]
HTTP: A protocol used to transfer data over the internet [1]
HTTPS: A variant of HTTP with an added layer of security that uses encryption to secure data transferred between a user and a website server [1]
Hulu: Video streaming subscription service
iCloud: Apple’s cloud storage platform
Image Search: A search function available on Google or tineye.com where you can search using an image; This is a very good tool if you are considering online dating since you can search an image of a person to see if they are a real legitimate person or a fake/scammer that is using someone else’s photos
Indexing: The organization of data, such as on a website, in order to streamline data
Infographic: A picture that contains educational information, statistics, and/or instructions that are accompanied by images and graphs (example below)
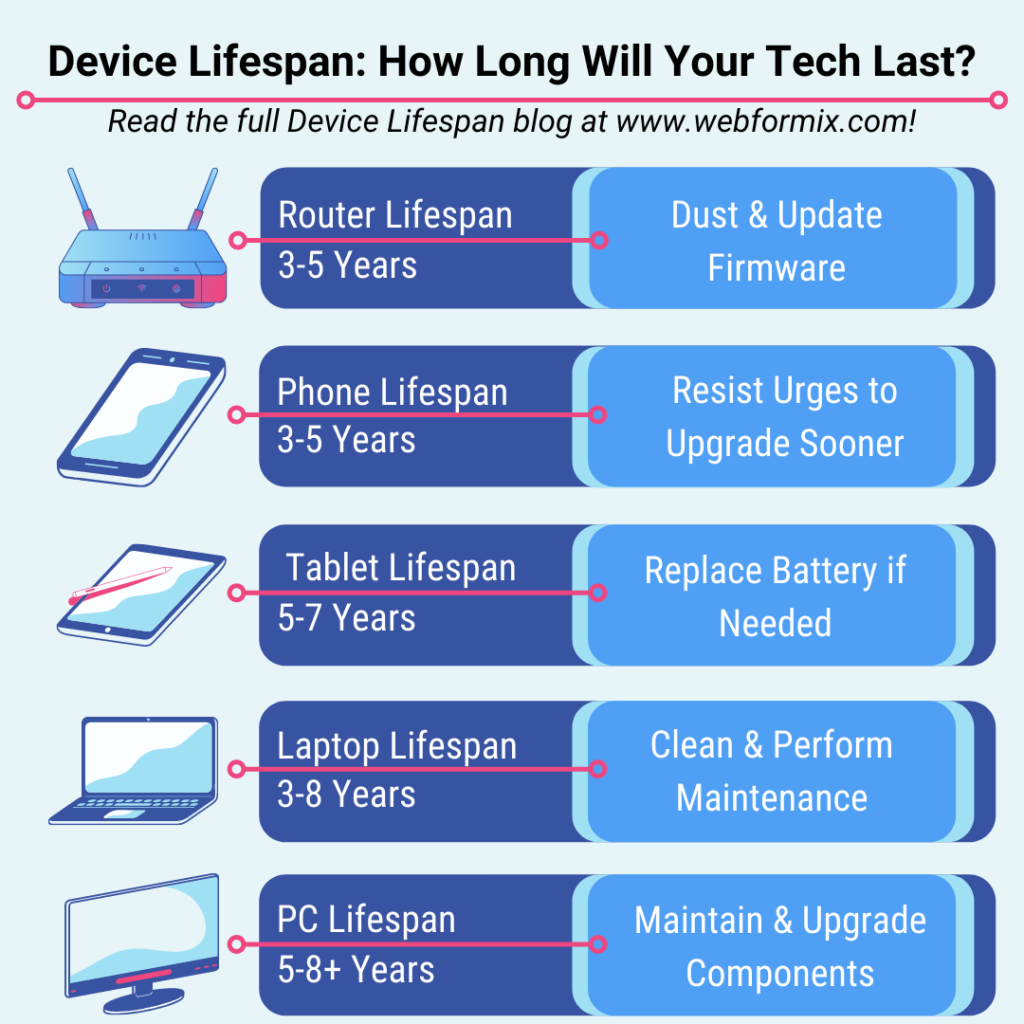
Internet: A globally connected network; See also world wide web
Internet of Things (IoT): Computing concept of the idea of wirelessly connecting devices in an environment to work together and communicate data that they can respond to [1]. Example: Smart home devices
Instagram: A social network that is image-based; Owned by Facebook
iOS: Apple device operating system
IP Address (Dynamic): A number that identifies your network connection and ties it to a geographic location; Changes after a period of time unless you have a static IP address; Can be hidden using a VPN
J, K: Tech Terms Defined
Java: A programming language used to create objects such as graphic interfaces and interactive elements on web pages, if you do not have Java installed on your computer it may not load webpages correctly
Jitter: A delay in receiving a packet of data, especially relevant for VoIP troubleshooting (follow the link to view instructions for jitter testing)
JPG: An image file format
Keyboard Shortcut: A combination of keys that can be pressed to execute a command instead of using a mouse or menu option. Example: control+x to cut and control+v to paste
Kilobit (Kb or kbit): 1000 bits; See also “Bits and Bytes: Measuring Bandwidth vs File Size“
Kilobits Per Second (Kbps): 1,000 bits per second; 1,000 Kbps = 1 Mbps
Kilobyte (KB): 1000 bytes; See also “Bits and Bytes: Measuring Bandwidth vs File Size”
L: Tech Terms Defined
Lag: A broad term used to describe a delay when entering or retrieving data; May indicate latency, packet loss, or weak wireless signal connectivity. Examples: Delay when typing and when words appear, delay in mouse movement, delay in loading websites or downloading data
LAN (Local Area Network): A computer network that covers a small area; Consists of multiple devices such as computers, printers, and scanners that can share data; Example: A home network with computers, phones, a printer, a Smart TV, and Bluetooth speakers that share a wireless internet connection and can access each other
LAN Party: A gathering of gamers who convene at one location, connect to one local area network, and proceed to play online games with each other for an extended period of time; See also “How to Host a LAN Party“
Link: Clickable text that leads to another website or webpage, usually appears underlined and in a different color than normal body text.
LTE (Long-Term Evolution): A standard for wireless broadband communication for mobile devices and data terminals [2]
Land Line: A copper telephone line that is wired into a building
Laptop Computer: Unlike a PC which has two parts, a monitor and tower, a laptop contains the computer boards under the keyboard and trackpad, and has a screen that folds open; Laptops can have a solid-state drive or traditional hard disk drive
Last Mile: “Last mile” refers to areas that are just outside of the range of established internet and telecommunications infrastructure; People with property in the “last mile” may need to pay telecommunications companies out of pocket to extend their infrastructure to the property
Latency: The amount of time it takes a packet of information to get from one place, to another, and back to the originator. If a person’s bandwidth is being maxed out by one application, it may cause the latency to increase for other applications that have to “wait in line” before being allowed through. Read more on latency vs bandwidth.
LCD: Liquid crystal display technology; Innovated digital displays that formerly used bulkier technology with lower resolution. LCD displays are light, thin, and use less electricity [1].
LED: Light-emitting diode technology; Newer than LCD, LED displays and lighting have a long lifespan and are very energy efficient
Left Click: To click the left button on a mouse; This button will activate an interactive element and/or allow you to highlight elements and navigate computer interfaces
License (Software): An agreement that grants usage rights for digital property
Line of Sight (LoS): A type of signal propagation that requires there to be no obstacles like hills or trees between the receiver (radio antenna) and the signal origin (communications tower); Fixed wireless internet requires line of sight
Live Stream: A video stream that is transmitting video as it is recorded in real-time
Load Balancing: A method of managing internet traffic by balancing it across different servers to avoid congestion that slows down the internet
Localization: Pinpointing a cell phone user’s geographic location based on their interaction with different cell phone towers [1]
Log File: Records communication between the operating system and software applications [1]
M: Tech Terms Defined
MAC Address: Short for media access control address; A unique identifier that is assigned to a network controller (such as a router) [2]
MacBook: Apple’s proprietary laptop
Mac OS: Apple’s proprietary operating system that runs on its devices
Macro: Automated input sequence that imitates keystrokes or mouse actions; Shortcuts that save time when conducting repetitive tasks, used often in Microsoft spreadsheets and word documents, also used in video games and SEO
Machine Learning: One aspect of artificial intelligence is machine learning, where algorithms can identify patterns and relationships in data and use that information to make itself more accurate
Malware: Malware (short for malicious software) is a general descriptive term for any software that seeks to do things such as damage your computer or collect personal data. A virus is always malware, although malware isn’t always a virus.
Megabit (Mb): One million bits or 1,000 kilobits; See also “Bits and Bytes: Measuring Bandwidth vs File Size”
Megabits Per Second (Mbps): Not the same as MBps; Equivalent to 1,000 Kbps (1,000 times faster); Measurement of data transfer rate. See also “Bits and Bytes: Measuring Bandwidth vs File Size”
Megabyte (MB): One million bytes or 1,000 kilobytes; See also “Bits and Bytes: Measuring Bandwidth vs File Size”
Megabytes Per Second (MBps): Measurement of data transfer rate; One megabyte is technically equal to 1,048,576 bytes, but in networking, it refers to 1 million bytes [1]
Megahertz (MHz): Measurement unit for the speed of electronic devices; Equivalent to one million hertz [1]
Megapixel (MP): Measurement unit for describing the resolution of a camera or image; Equivalent to one million pixels [1]
Meme: A captioned GIF, picture, or video clip that is funny or satirical, can also be used to describe behaviors or styles; Memes are shared online and can “go viral” then go out of style very quickly
Memory: The part of the computer that stores information; Types of memory include RAM, ROM, and RWM
Mesh Network: A network where devices such as a router and node devices act as a relay system to transmit data in a more efficient path [1]
Metadata: Data that describes other data, such as descriptions that describe website content [1]
Microsoft: A giant technology company that produces products such as the Windows operating system, Microsoft Office (Word, PowerPoint, Excel), Microsoft Edge internet browser, and hardware like laptops
Modem: Used with cable internet and DSL internet; A device that converts data produced by a device into a format that can be transmitted through a telephone line or cable line
Moderator: A user of a social media platform or message board that reviews content to enforce community guidelines
Monitor: Also know as a computer screen; Detachable visual display for a computer
Motherboard: The main circuit board of a computer that enables crucial communications in the computer’s system; Contains RAM and CPU with expansion slots for add-ons
Mouse: A device that allows you to control an on-screen cursor with hand movements; Old versions had a ball inside, new versions are largely optical mice; Laptops generally have a trackpad instead of a mouse
MP3: Music file format
MP4: Video file format
MS-DOS: A very old type of computer operating system that is only text and no graphics, commands are entered in command lines
MSN (Hotmail; Outlook): A free email service
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): A security mechanism where multiple types of user validation are required, can include physical mechanisms like inserting a card, biometric mechanisms like fingerprint verification, and logical mechanisms like a PIN number
Multimedia Message Service (MMS): Mobile content exchange, SMS only supports text for text messaging on cell phones, but MMS supports sending text, images, video, and sound
N, O: Tech Terms Defined
NAT (Network Address Translation): One function of a router that enables public and private network connections and allows single IP address communication [1]
Netflix: Video streaming subscription service
Net Neutrality: The principle that Internet service providers must treat all online traffic equally, and not discriminate or charge differently based on user, content, website, platform, application, type of equipment, etc. [2]
Network: A broad term used to describe a group of two or more connected devices or nodes that can communicate; Can describe accessing the internet via an internet service provider’s infrastructure, shared software, or refer to a home or office network
Network Address: A unique identifier of a device within a network such as an IP address or MAC address
Node: A signal redistribution point or endpoint
Number Lock (Num Lock): A key that says “Num Lock” that is located on keyboards with a number pad, You need to press it on in order to use the number pad
Office Suite: A Microsoft software suite that includes Word (a word processor), Excel (spreadsheets), and PowerPoint (presentations)
Offline: Not connected to the internet
Offline Browsing: If you are offline but open your internet browser you will still be able to view downloaded material and some material that may be stored in your browser history
Open Source: Source code that is made freely available for possible modification and redistribution [2]
Operating System (OS):
Optical Mouse: Originally, a mouse had a ball underneath a top plate with buttons, modern mice have an optical element and sensor that transmits movements instead of a ball
Organic Search: As opposed to paid search, search engine results that naturally rank well and are suggested when you enter a search term. Websites compete for appearance on the first page of search engines and are ranked according to their content quality and other search engine optimizations
P, Q: Tech Terms Defined
Packet Analyzer: A computer application used to track, intercept and log network traffic that passes over a digital network [1]
Packet Loss: Occurs when not all packets of data that are sent are received; Results in jitter, interruptions, or loss of service [1]; A performance metric, especially for VoIP
Paid Search: These search results are the first listings you see when you enter a phrase or word in a search engine. However, they are only there because they are paying to be shown when those search terms are entered and may not be the most relevant websites. If you click to visit them, the owner will be charged. Organic search results will be shown below paid search and are likely more helpful resources.
Passphrase: Similar to a password, but instead of one word it is a long sequence of words used to access an online account which provides enhanced security
Password Manager: A software feature, extension, or plug-in that remembers your user names and passwords. You should avoid using the password manager in your internet browser because it is easier for hackers to gain access. Instead, use a plug-in like LastPass with a separate password that you never write down or save in your browser. Never re-use your passwords, have a unique one for every website.
Payment Gateway: An online gateway, usually a subdomain of a website, that features enhanced security for checkout when you are shopping online
PDF (Portable Document Format): Cross-platform document format with color-accurate information; Can include text and/or image(s) and is highly compressed [1]
Personal Computer (PC): Consists of a computer tower and monitor, also called a desktop computer
Phishing: A scam that uses spoofing (legitimate-looking emails, texts, or social media posts) to trick users into revealing personal data such as login information for their accounts or financial information so the scammer can steal the user’s identity or money.
PHP: A scripting language used to create dynamic and interactive HTML webpages [1]
Pixel: The smallest element in a digital image; Unit of measure
Planned Obsolescence: A corporate policy of artificially limiting the useful lifespan of a product, or intentionally designing it to be non-durable
Ping Test: You can measure latency by doing a ping test. Anywhere from 0 to 50 milliseconds (ms) is excellent to average. Streaming and gaming will start to have issues after that. 50 to 100ms is still usually ok for web browsing, but over 100ms will be noticeably slow and frustrating. Instructions: “Internet Bandwidth vs Latency“
Platform: A computing platform is an online environment, app, or software program; Examples: Operating systems like Android or Windows, digital interfaces like social media, hardware like Apple’s devices
Player Versus Player (PvP): A type of game where players compete against each other instead of against the game itself (or against non-player characters)
Plug-In: Also called a browser extension; A software program that you can install in your internet browser for added functionality. Examples: LastPass password manager, Grammarly grammar and spell checker
Point-to-Point System: A system that expands the range of your internet to additional buildings on the property; Also called a point-to-point wireless bridge
Power Cycle: To turn a device off and then turn it back on again; Related article “How to Bypass Your Router & Power Cycle Equipment“
Power Over Ethernet Cable (PoE): Power supply used with Webformix radio antennas
PowerPoint: Microsoft Office program for making presentations; .ppt file extension
Power Supply: A device that usually has a cord; Used to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power a device [2]. Examples: Computer cord with block box in the middle, PoE for Webformix radio antennas
Power Surge: A sudden surge in electrical voltage (such as from a lightning strike) that can damage electronics, prevented by using a surge protector
Prime (Amazon): Amazon membership program with benefits of questionable quality for the price
Prime Video: Amazon video streaming service with free content for members, and paid options for members and non-members
Private Message (PM): Message sent directly between two users or a defined group of users; Same as a direct message
Processor: An electronic circuitry that is integrated into a computer to perform arithmetical, logical, input/output (I/O), and other basic instructions from the computer’s operating system [1]
Program File: In Windows, the file where third-party applications are installed by default [1]
Programming: The work of writing codes in programming languages in order to create programs, software, platforms, websites, and apps
Programming Language: A language of “code” that computers are able to understand, used by developers to create programs
Proxy Server: A server application that acts as an intermediary between a client requesting a resource and the server providing that resource [2]
Public Folder: A folder on your computer that is visible and accessible to other devices on your network
Public IP: The IP address for your device that is recorded when you visit websites, also the IP address for a website that is publicly visible
Push Alert: Also called push notification; A notification, usually a banner pop up on a phone, that is displayed to alert you of an action of interest in an application or for marketing purposes; Examples: Text message notification, News alerts, Alerts about social media activity. When a red dot appears on an app, that is a badge notification
Query: A request, written in computer code, for information from a database that is returned by SQL or as a graph or other display
Quick Response Code (QR Code): Like a square version of a barcode; QR codes can be scanned using the camera on a smartphone, when detected a pop up on the phone screen will prompt you to go to a linked website
QuickTime: Apple’s proprietary multimedia framework for playing videos, movies, sounds, and viewing images
QWERTY Keyboard: Thee most common keyboard format that has been used since typewriters
R: Tech Terms Defined
Radio Antenna: An antenna for receiving and transmitting radio frequencies such as those used to provide fixed wireless internet service
Radio Frequency (RF): The rate of oscillation of electromagnetic radio waves in the range of 3 kHz to 300 GHz and the alternating currents carrying the radio signal [1]. Different radio frequencies are used for Bluetooth, WiFi, television, garage door openers, baby monitors, FM radio, AM radio, with 2.4 GHz being the most popular because it is unregulated.
Radio Frequency Field (RF Field): A field of radio waves with an alternating current that produces an electromagnetic field when passed through an antenna, different spectrums are used for different purposes
Random Access Memory (RAM): A type of computer memory located on the motherboard that is used to store information for quick access and short term storage [1]
Ransomware: A malware program that takes over your computer, encrypts your files, and locks you out of the system until you pay the hackers a ransom, usually in the form of cryptocurrency; Occurs via downloads and email attachments that secretly contain the ransomware program [1]
Raspberry Pi: A low-cost computer with a single circuit board that runs on open-source software allowing it to be used for customized tasks and education
Read-Only: A file format that allows you to open and view a file but will not allow you to edit or make changes to the file; To change a read-only file, you must save a separate copy
Read-Only Memory (ROM): A type of computer memory that can be read from but not written on; Permanently stores information that is essential to device function [1]
Read-Write Memory (RWM): A type of computer memory that can be read from and written on [1]
Readme: Readme files can be attached to software or other downloads and provide additional instructions about using the file
Reboot: To restart your device (“boot” or “boot up” is a term for the operating system screen you see when the device is starting up and loading the operating system)
Recycle Bin: When you delete a file or folder on your computer, it is stored in the recycle bin. To delete it completely, you must empty the recycle bin.
Refurbished: A used product that has been restored to “like new” condition
Registry Cleaner: On the Windows operating system, a third-party utility that removes redundant items in order to keep the operating system working without errors; Good to run if your computer is taking a long time to boot up or is running slow and/or encountering operating system errors
Reload (Refresh): Keyboard shortcut to reload the window open in your internet browser is the F5 key; Updated the webpage to reload elements that may have changed or not loaded properly
Remote Access/Remote Desktop: Software that allows you to access another computer in a different location. Never let a person who calls you “remote in” to see your screen! Tech support will never call you unless you have contacted them directly, this is a very popular scam! Be suspicious of anyone that offers to remote into your computer and do not give them access unless you are 100% sure they are a legitimate professional responding to a request you have submitted. When you submit a help request, not information like the date and time you sent it or a confirmation number. Use that information to verify the person is a legitimate representative.
Repeater (Signal Repeater): A device that re-transmits a signal to amplify and extend it over a further range, also known as a signal booster
Reply (Email): Email response sending option that replies to the person who sent the original email
Reply All (Email): Email response sending option that replies to all people an original email was addressed to and the original email sender
Rich Text Format (RTF): A format for a word processing document that is compatible with multiple word processing programs
Right Click: Clicking on the right button on a mouse will open up a menu that contains actionable options
Roaming: In relation to cellular services; Roaming provides connectivity outside of your provider’s coverage area but may result in additional fees from the use of another provider’s network
Router (Wireless Router): A router is an essential piece of an internet connection that analyzes data packets that are being transmitted from one network to another; Provides wireless connectivity (WiFi). Related article “Understanding Your Wireless Internet Router“
Router Firmware: Software that is pre-installed on routers to manage its operating protocols and security [1]
RSS Feed: A news feed that users can subscribe to; RSS feeds are delivered in XML format and read through an RSS reader program
Runtime Error: An error that occurs when executing a program, not an error related to the computer’s operating system [1]
S: Tech Terms Defined
SaaS (Software as a Service): A business that rents or leases storage space to other companies
Safe Mode: When booting up your computer, especially after a crash, this option loads a diagnostic interface of the operating system for troubleshooting purposes
Satellite Dish: Bowl-shaped antenna for receiving transmissions from a satellite orbiting the Earth; Used for TV and internet; Not the same as a radio antenna for fixed wireless internet but they do look similar
Satellite Internet: Internet served over a satellite dish that connects to a satellite in space; Know to be expensive, have latency issues, and lose functionality during weather events
Scanner: Hardware that is used to digitize documents or photos
Screen Capture (Screenshot): The keyboard shortcut window button + shift + “s” will allow you to take a picture of your computer screen that can be pasted into a paint program and saved as an image
Screen Sharing: Allows others to view what you see on your computer screen; Often used in videoconferencing and for IT help. Never let a person who calls you “remote in” to see your screen! Tech support will never call you unless you have contacted them directly, this is a very popular scam!
Scrolling: The act of navigating down a website or social media feed to view more content
Scripts: Lists of commands executed by certain programs or scripting engines; Used to customize and automate repeated tasks and control overall computer functions [1]
Search Engine: A website where you enter a phrase or keyword and links to relevant content appear. Examples: Google, Bing, Duck Duck Go, Brave
Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Consists of activities that make websites more visible in search engines and increase search rankings; Examples: Keyword optimization, link building, website indexing
Security Software: Software such as Norton Antivirus that protects your device from malicious activity online such as hacking, viruses, and malware; May also be a built-in part of your computer’s operating system
Secure Digital Card (SD Card): A non-volatile form of large-capacity memory for portable and mobile devices; Used in phones; tablets; and digital cameras; Three types: MicroSD (15 mm × 11 mm), MiniSD (21.5 mm × 20 mm), and SD (32 mm × 24 mm) [1]
Server: Device, computer, or program used to manage network resources; Servers can do many things such as host websites, transmit data, control access, and send and receive email
Sling: A video streaming service that offers on-demand shows and live television; Has a subscription model similar to cable packages
Smart Home Device: A home device that has the ability to connect to the internet, often pairs with a smartphone app
Smartphone: A cellular phone with mobile data and WiFi ability that functions like a phone plus a mini-computer
Smart TV: A television that can connect to the internet; Features often include pre-installed streaming apps, an app store, a web browser, and the ability to be controlled by your smartphone
Snapchat: Social media platform where pictures, videos, and messages expire after a certain amount of time
Snippet: A re-usable piece of code for a small function that can be put into a large codebase [1]
Software: General term used to describe computer programs or programming tools that perform specific tasks or processes; Hardware is a physical device whereas software is not a physical object (though it may come on a compact disc)
Solid State Drive (SSD): An alternative to hard disk drives (HDD); SSD’s store information differently than HDD’s for faster and more reliable performance; Computers with solid-state drives tend to be more expensive and higher quality
Spam: Unwanted or unrequested emails; More broadly refers to undesirable and obnoxious advertising that is invasive to the digital experience; May also be linked to malicious activities like phishing and spoofing
Spectrum Analyzer: Tool used to measure signal strength and frequency range for radio frequencies [1]
Spoofing: Maliciously disguised websites or emails that are made to look authentic but will mislead the recipient or user into divulging personal data, may be used as a tool in a phishing attack
Spotify: Music streaming platform; Pandora is a competitor that also streams music
Spyware: A malicious program that is secretly installed on your computer to track what you do and gather your personal data
SQL: A programming language for managing and retrieving information from databases
SSID: The name of a WiFi network that is visible when you open your network connections
SSL Certificate: Small data files that protect sensitive information transmitted on the internet, used to authenticate a website by proving domain ownership
Standard Definition (SD): The lowest quality video resolution available; 480p video mode. See also “Wireless Internet Streaming Guide”
Static IP: A permanent IP address (vs normal dynamic IP address) that is used to identify a device on a network.
Storage Capacity: A computer has a storage hierarchy that consists of primary storage (CPU and RAM), secondary storage (hard disk storage), tertiary storage (near to online storage; tape libraries; writable CDs), and offline storage (portable hard drives, removable storage). Your computer’s storage capacity is the total amount of space on your CPU, hard disk drive, memory cards, and other storage spaces not built into your computer like portable hard drives or cloud storage drives.
Storage Provisioning: Assigning space in your computer’s drives that are allocated for storage purposes to optimize computer performance
Streaming: Online on-demand delivery of content such as recorded video, live video, and music
Subdomain: Address for a specific subsection of a website; Example: southernoregon.webformix.com. An alternative to using a subdomain is to use a subfolder structure. Example: webformix.com/southernoregon.
Surge Protector: Device used to protect electronics from unexpected voltage spikes; Read more in our article “Why Do I Need a Surge Protector for My Router?”
SVGA Monitor: A monitor that uses the Super Video Graphics Array (SVGA) standard and has a screen resolution of 800×600 pixels [1]
Syntax Error: A error associated with coding/programming that is detected by a program called a compiler [1]
System Administrator (SA): A person who manages, maintains, and oversees a multiuser digital environment
System Backup: A copy of an operating system and its user’s files that can be used to restore the system if it becomes corrupted or deleted
System File: A file that is critical for the operation of a computer system; Example: Windows System32 folder
T: Tech Terms Defined
Tablet: A mobile device that is essentially a very large smartphone crossed with the capabilities of a laptop; They are a single screen with no built-in keyboard or mouse
Tabbed Browsing: Instead of opening multiple browser windows, you can open multiple tabs in one window, each with a different website on it
Tag: A description, such as a keyword, that is attached to a piece of content and describes the content succinctly
Task Manager: A utility on your computer that displays all of the programs and processes that are running and how many resources they are using; Accessible through the keyboard shortcut where you press control-alt-delete
Teleconference: A meeting held via telephone where multiple people can all connect from separate sites
Temporary File: A file that holds data prior to a permanent version being saved. Example: If Microsoft Word crashes, it will ask if I want to restore the document I was working on when the crash occurred but some data may be lost
Terabit (Tb): Measurement for 1 trillion bits
Terabyte (TB): Unit of digital information storage equivalent to 1,000 gigabytes, or 1,000,000,000,000 bytes
Terabytes Per Second (TBps): Extremely fast data transmission rate equivalent to 1,000 gigabytes, or 1,000,000,000,000 bytes per second [1]
Terahertz (THz): Measure of frequency that is equal to 1 trillion hertz
Terms of Service (ToS): Usage agreements implemented for websites, software, and operating systems limit legal liabilities and set rules for usage parameters and conduct; Very long small text documents that no one reads and there is no option not to agree to
Text to Speech (TTS): Language modeling programs that allow text to be converted to speech automatically; Traditionally used to improve accessibility for the visually impaired but now becoming popular for use in dubbing online videos (replacement for hiring voice actors)
TikTok: A video-based social media platform
Top-Level Domain (TLD): Also known as domain suffixes; Refers to the last section of a URL that comes after the dot; Generic and country-specific domains both exist; Examples: .com, .org, .edu, .net, .biz, .gov, .uk
Tor (The Onion Router): Originally developed for the U.S. Navy to protect government communications; Open source security and privacy software; Specifically protects against a type of internet surveillance called traffic analysis, helps hide your identity online. Available at https://www.torproject.org/
Torrent: A type of file used by BitTorrent to direct access and authorization for the peer-to-peer sharing of media
Trackpad (Mousepad): Flat pad on a device like a laptop that allows you to navigate on-screen by tracing your finger movements and moving the cursor accordingly
Tweet: A post on the Twitter social media platform that has a limited number of characters; If you “share” someone else’s tweet, it is called “retweeting”
Twitter: Social media platform where users can post “tweets” of 140 to 280 characters or less and share media like photos and videos
Two-Factor Authentication (2-FA): Enhanced security feature that requires two types of verification to demonstrate that you are the authentic account owner
U, V: Tech Terms Defined
Ubuntu: Open-source operating system based on the Debian GNU/Linux distribution; Used mainly by developers
Ultra High Definition (UHD; 4K; 8K): Display resolution of at least 3840 by 2160 pixels, up to 4096 by 3112 for 4K, and up to 7680 by 4320 for 8K [1]; Provides very high-quality video but requires more bandwidth; See also “Wireless Internet Streaming Guide“
Unicode: A standard for the representation of common text and symbols of any language in digital and print media [1]
Uninstall: To remove a program or application
Unlocked Cellphone: A cellphone that will work with any service provider; Most commonly applies to Apple devices; Can leave a phone vulnerable to security threats
URL (Uniform Resource Locator): The address of a specific resource on the internet; Most commonly thought of as address for a website (the part you type in the bar at the top of your internet browser); Examples: IP address, a website domain name such as www.webformix.com
URL Redirect: A webserver function that forwards you to another web page if the URL you were navigating to is no longer available; If a redirect is missing, you see a 404 Error
USB (Universal Serial Bus): A type of connector on the end of a cord with a wide range of uses; Comes in different sizes such as micro USB or Macro USB; Examples: Charging cords, cord to connect a device to your computer
User Interface (UI): A broad term to describe the visual and functional aspects of a website, platform, or program that encompasses the features which users interact with; Example: The user interface of Windows 8 was frustrating for many people because common features were difficult to access and the design was ugly
Username: The unique alias you use when accessing a personalized account; May also be your email instead of an alias
Vector Graphic: Graphical representations of mathematical objects such as lines, curves, polygons, etc.; Very high-resolution scalable graphics; .svg file extension
VGA Cable: Type of computer cable that carries visual display data from the computer’s central processing unit(CPU) to the monitor [1]
Video Blog (Vlog): A video presentation of blog material (articles) that provides viewers with a more interactive experience
Video Conferencing: Two or more sets of hardware and software interact while simultaneously transmitting and receiving video and audio signals from two or more geographic locations [1]; Examples: Zoom, Microsoft Teams
Virtual Private Network (VPN): Private network connection that is built over a public network infrastructure such as the internet; Utilizes security features such as encryption and hiding your IP address; Can be used for remote access
Virtual Reality: Virtual reality seeks to create seamless digital environments without the awareness of computer screens and hardware. Creating this illusion does require a VR headset to be used. When you wear a VR headset, you will obviously know that it is on your face. However, your presence inside the virtual reality world it projects will feel so realistic you may forget about the headset. Examples: Oculus Quest, PlayStation VR, HTC Vive Cosmos, and Valve Index. These headsets have LCD or OLED panels inside that create a 360-degree environment. In that virtual environment, you can move your virtual hands and body as if it were real life.
Virus: A virus is a small line of code that hides in a legitimate program or file. Specifically, it’s code that replicates itself and tries to spread to other computers on the network, much like a biological virus spreads from person to person. One of its favorite methods of replicating itself is sending a copy of itself to everyone in your email address book.
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP): A phone service that works over the internet; Instead of using traditional copper telephony, VoIP streams the audio over the internet; Not flawless and not good for critical applications where the phone needs to be 100% dependable; Good for spending a lot of time chatting on the phone. Further reading: VoIP Troubleshooting Guide, Webfomrix VoIP Service
W, X, Y, Z: Tech Terms Defined
Webcam: A camera that is built into your computer (laptops), or connected via USB so you can record video of yourself or stream video of yourself
Webinar: An online seminar usually conducted using video conferencing
Website: A single web domain with multiple web pages that contain content
Whitelist: Opposite of blacklist; To list a particular email or website as safe by manual configuration; Example: Marking a sender “not spam” in email
Wide Area Network (WAN): A network that exists over a large-scale geographical area to connect multiple smaller networks such as local area networks (LAN); Uses a protocol called TCP/IP, and devices such as routers, modems, and network switches [1]
WiFi: Does not actually stand for wireless fidelity or wireless field; WiFi is a wireless connection to the internet
Wikipedia: Online encyclopedia that has entries created and edited by their users
WiMAX: Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access; Wireless broadband communication standards based on the IEEE 802.16 set of standards, which provide multiple physical layer (PHY) and Media Access Control (MAC) options; Harmonized standard for wireless communications
Window (Browser Window): When you open your internet browser a window appears. You have the option of opening multiple browser windows or opening multiple tabs if you want to view more than one website at a time.
Windows (Operating System): Microsoft operating system that is standard on all non-Apple computers
Wireless Access Point (WAP): Hardware device or configured node on a local area network (LAN) that allows wireless and wired devices to connect to a network such as the internet; Consists of antenna and radio transmitters, also known as a hotspot
Wireless Adapter: Hardware device that provides wireless connectivity to computers that do not have built-in WiFi connectivity
Wireless Bridge: Networking device that allows to different segments of the local area network (LAN) to be wirelessly connected via fixed wireless
Wireless Charging: The electrical charging of a battery-powered device without a wired connection; Three methods include inductive charging, radio charging, and resonance charging [1]
Wireless Internet Service Provider (WISP): An internet service provider that brings people the internet by distributing signals from a communication tower to a radio antenna that is mounted to the client’s roof. Fixed wireless internet travels on the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz radio wavelengths. A good option for rural internet service (as well as urban).
Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN): A wireless distribution network that utilizes radio waves to distribute internet connectivity for two or more devices over a coverage area such as a small home or office; Coverage range depends on the signal strength and the area it is rated for; WiFi refers to a given wireless connection whereas WLAN refers to the network itself that consists of access points and clients [1]
Wireless Mesh Network (WMN): Transmits data using a mesh network; In a wireless mesh network, there are multiple mesh nodes that act as routers to propagate data [1]
Wireless Wide Area Network (WWAN): A specific type of network that sends wireless signals beyond a single building or property; local area networks (LAN) and WWAN differ in the type of technology used and the distance they cover with WWAN often using cellular network systems to send signals over a longer distance [1]
Word Document: Text document with a .doc or .docx file extension, they are made in Microsoft Word (can also be made or viewed in Open Office or Google Docs)
WordPress: Open source website and content publishing platform
Word Processor: Program for creating text documents such as Microsoft Word, Open Office, or Google Docs [2]
World Wide Web (WWW): Network of online content that is formatted in HTML and accessed via HTTP; Originally designed in 1991 by Tim Berners-Lee [1]
XML (Extensible Markup Language): Document format for spreadsheets (.xml); Markup language that defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable [2]
Yahoo: Search engine, news, and email website
Yelp: Review website where customers post reviews of local businesses and services
YouTube: Website and app for watching, uploading, and sharing videos
Zip Drive: Medium-capacity and portable magnetic disk storage system launched by Iomega in the mid-1990s [1]
ZIP File: Compressed file that you “unzip” to get to uncompressed versions of the file



Recent Comments