When you are browsing the internet it is common to encounter a pop-up that asks you to accept website cookies (HTTP cookies). The newer cookies pop-up will even ask you which cookies you would like to allow. But do you really need to allow cookies at all? In some cases, you will need to allow cookies in order for a webpage to work correctly. In other situations, you can definitely go without them. Let’s take a closer look at website cookies to learn what we need and what we don’t!
What Are Website Cookies
A website cookie is information that websites collect and store in your internet browser. That information helps the website remember your device in the future in case you return. Cookies collect information about what you view and what activities you do on a website. This includes remembering your login information, remembering what you have in your shopping cart, and tracking your preferences.
Benefits of Website Cookies
- Remembers your login
- Stores your shopping cart
- Customizes your experience
- Creates ads that are targeted to you (maybe a downside also)
The Downside of Website Cookies
- Transmits information back to the website owner’s server/computer
- May contain personal data
- May happen without you knowing unless alerts are set up in your internet browser
- Possibly vulnerable to hacking and malicious activity
- Cookies can be inaccurate in identifying users on computers or browsers with multiple accounts
- “Back” button can generate inconsistencies in cookies
Types of Website Cookies
Not all HTTP cookies were created equally. They all have different functions and different durations. Depending on the type of cookie, it may also be more or less secure. Here is a short overview of the different types of cookies to help you better understand what you may be “allowing.”
Authentication Website Cookies
Authentication cookies are used to verify users when they log into a website. This prevents you from having to log on individually to every page that contains sensitive information. However, authentication cookies are not always secure. The security of the website and the encryption of the cookie data will determine just how secure an authentication cookie is. If these cookies are not properly secured, they can fall into the hands of hackers. If authentication cookies fall into the wrong hands they can allow hackers access to user data and allow them to gain access to the website that owns the cookie.
Single-Session Website Cookies
Single-session cookies are only recorded temporarily and are erased when your session ends or when you close your internet browser. These cookies only help with website navigation and are enabled by default.
Multi-Session (Persistent) Cookies aka Tracking Cookies
Persistent cookies record your information over multiple websites and remain on your computer. You need to manually delete persistent cookies in order to get rid of them. If you do not delete them they will occupy space on your hard drive forever, or until they expire. It can take months or even years for them to expire though.
Sometimes persistent cookies are also called tracking cookies. Tracking cookies, especially third-party tracking cookies, compile long-term records about your online habits and activities. This is a huge privacy concern for many which have prompted lawmakers to require the informed consent of users prior to storing non-essential cookies on their device.
Secure Website Cookies
Secure cookies can only be transmitted over encrypted internet connections (HTTPS) and cannot be transferred over unencrypted internet connections (HTTP). This is important because when cookies are sent over an unencrypted connection they are vulnerable to security threats like hackers “eavesdropping” or stealing cookies.
HTTP-Only Cookies
Another way to eliminate cookie theft is by using an HTTP-only cookie that can only be accessed on client-side APIs like JavaScript. However, this still leaves cookies vulnerable to security threats other than theft. These include forgery and tracing cross-site attacks.
Same-Site Cookies
These new cookies were introduced in 2016 by Google Chrome. Same-site cookies can have three settings: Strict, Lax, or None. Those settings restrict where cookies can be sent to and mitigate some security threats.
Third-Party Cookies
A first-party cookie has a domain attribute that is the same as the domain in the web browser address bar. Third-party cookies belong to a domain different from the one you are visiting. These are common on websites that have content from external websites. The concern with third-party cookies is that they create the potential for your browser history to be tracked and used by advertisers. Most web browsers will have a setting that allows you to block third-party cookies. You should turn that on unless you are on a particular site that needs third-party cookies enabled for the functionality of features.
Supercookies
Supercookies are blocked by most web browsers because they are a security concern. These malicious cookies have a top-level domain suffix (.com) or a public suffix (.co.uk). A normal cookie would be specific to a domain like webformix.com, but the supercookie is not specific so it can be used to fake logins or change user information.
Zombie Cookies
Malicious zombie cookies can be placed on a website server by a visitor. They are hidden outside of the normal cookie storage location and automatically recreate HTTP cookies as regular cookies when the original cookie is deleted. They are a huge browser security breach and are extremely difficult to remove. The information collected is very valuable to advertisers and hackers alike.
Should You Allow Cookies?
Cookies can improve website functionality and provide you with a better experience online. However, cookies also allow your online actions to be tracked across websites and shared with marketers. When you see a pop-up asking if you want to allow cookies, stop and read. Only allow the cookies that are absolutely necessary. Cookies can definitely be part of making your online experience enjoyable but accepting unnecessary cookies takes up space on your device and leaves you more vulnerable to security threats and advertisers.
Online Security & Managing Your Cookies
- Clear cache, history, browser data, and cookies if device performance is poor
- Delete your cookies at least every couple of months
- If your device is behaving unusually, take it to a computer repair professional ASAP
- If your device is behaving unusually, do not use it for anything that involves personal or financial information
- How to manage cookies in Chrome, Edge, Firefox, and Brave
Website Cookies Walk-Through
Many websites will have a pop-up that notifies you that their website uses cookies. Depending on the website, there are a couple of different types of pop-ups that you will encounter. This first example shows a simple cookie pop-up.
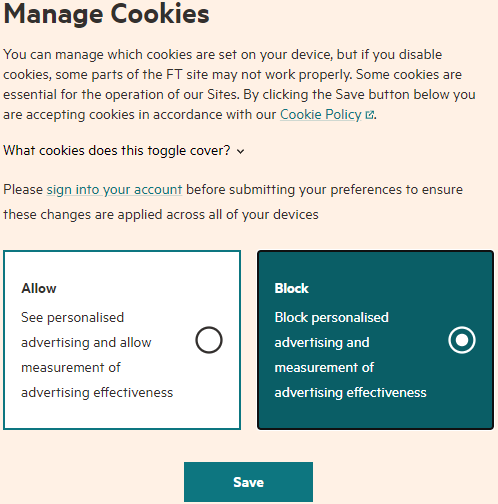
Simple Website Cookie Options
You have two options: Manage cookies or Accept & continue. Click “Manage cookies” to get to the cookies menu. Next, select “Block” to block cookies that collect data that would be used to target ads towards you (unless you really want to see personalized ads). Note that the site advises you to sign in so it will remember your cookie preferences. This may not be a feature on all sites, but it is for this example.
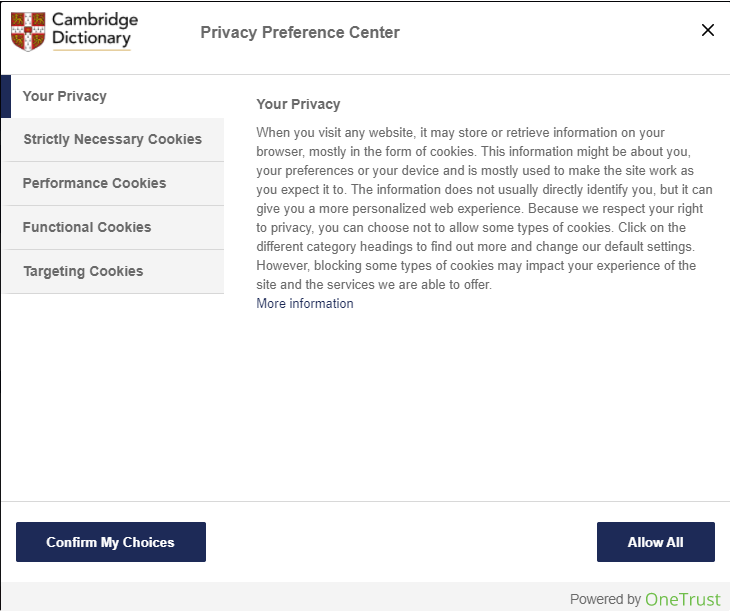
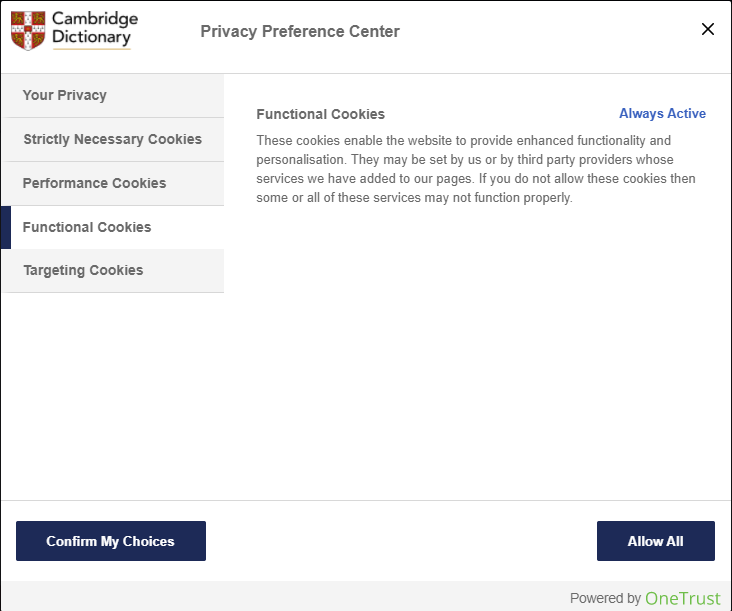
Advanced Website Cookie Options
In this second example, you have a website with a more privacy-conscious cookies policy. The first thing you see is this bar at the bottom of the webpage. Again, you have the choice to manage cookies or just accept them all. Since you want to avoid unnecessary cookies, click “Cookies Settings.”
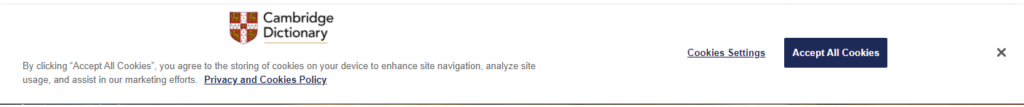
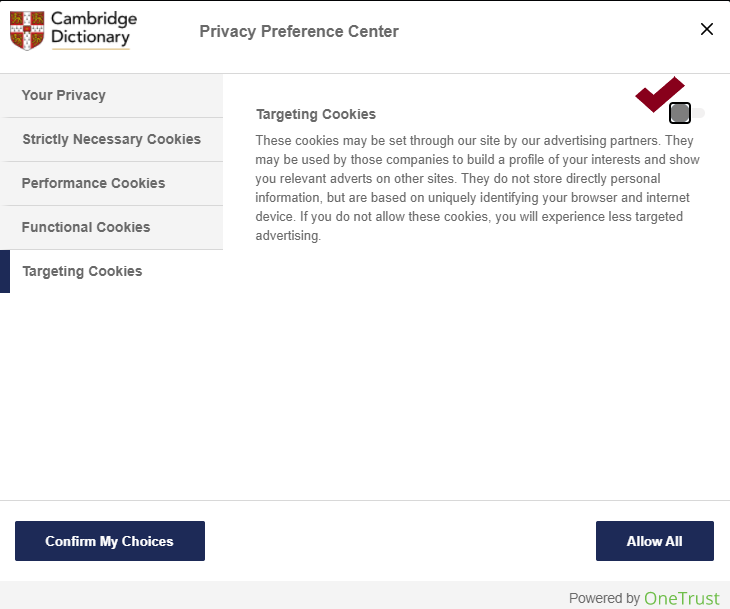
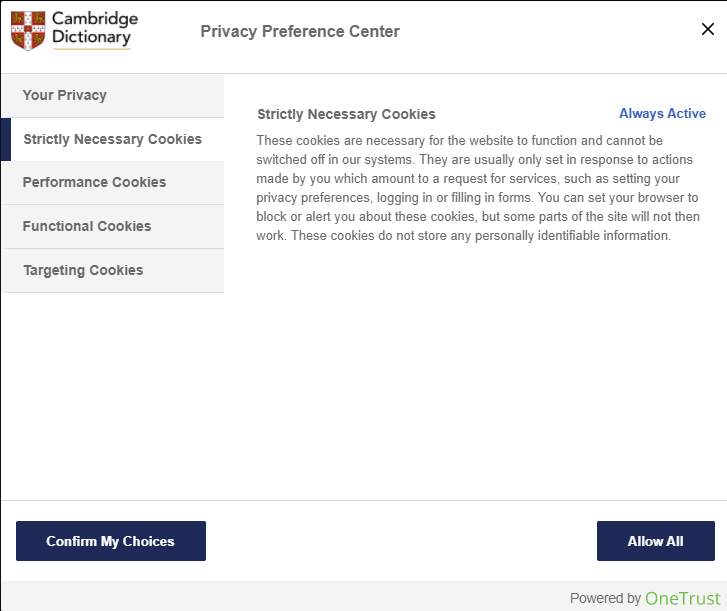
Next, you will see a menu that explains all of the types of cookies and presents you with options for turning some on and off. First, the “Your Privacy” section explains the website’s privacy policy to you. Second, it tells you about its “Strictly Necessary Cookies.” These do not have an option to turn them off.
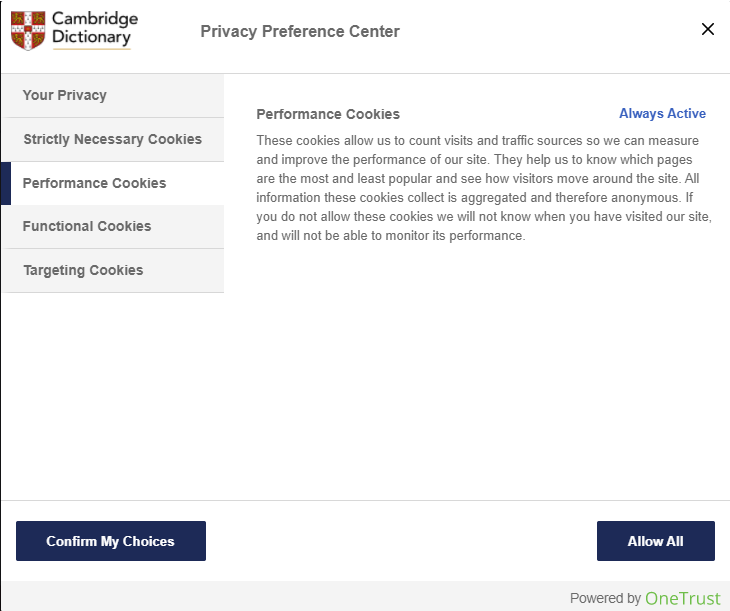
Third, you are told about the website’s “Performance Cookies” and “Functional Cookies.” These also do not have the option to be turned off.
Finally, we get to the “Targeting Cookies.” You are given the option to turn off these cookies. Click to make the slider button grey to turn them off. This will stop cookies that collect your data for advertising purposes. Every website is a little different, but taking the time to manage your cookies reduces data collection, enhances security, and improves the use of storage space on your device.



Recent Comments